Overview
In order to carry out the metabolism activities of the body’s cells efficiently, glucose is extremely important as it provides the requisite energy to the cells. When we consume food, the liver converts the food into glucose which is released into the blood.
Pancreas produces a hormone called insulin that operates as a supervisor to the sugar levels in blood. Its key responsibility is to preserve the blood sugar levels in a balanced ratio keeping it neither very high nor very low. Diabetes is a bunch of related diseases in which the body fails to regulate the blood sugar levels, especially glucose.
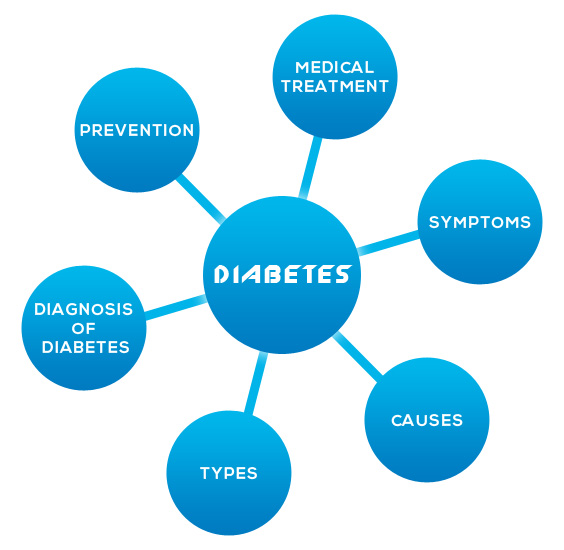
Types
Diabetes can be classified into two types namely 1) Type 1 diabetes and 2) Type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient amount of insulin or completely stops to produce insulin in order to maintain the glucose level in the blood. Whereas, Type 2 diabetes is when the body fails to use the insulin produced by the pancreas. Another form of diabetes called as gestational diabetes (GDM) is when the women that haven’t had diabetes in the earlier part of life show signs of high blood glucose levels at the time of her pregnancy.
Prediabetes is a common condition correlated to diabetes. In people with prediabetes, the blood sugar level is higher than normal but not high enough to be considered diagnostic of diabetes. According to a study, every year more than 200,000 Americans die of diabetes. Prediabetes is an alarm that signifies a person suffering from it, is not too far from entering into the core level of the disease. Those suffering from prediabetes pose a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes. However, one can get rid of prediabetes just by bringing in certain changes in his or her lifestyle. Increasing physical activity and losing a little weight can completely keep away from or delay the development of type 2 diabetes. Surprisingly, according to estimation, about one third of the adults suffering from diabetes are not even aware that they have contracted the disease.
Causes
In today’s scenario, obesity in association with the occurrence of sedentary lifestyle is one of the main reasons for the rapid growth of diabetes cases. Following are the factors believed to be responsible for the development of diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes is known to have a direct relation with one’s immune system. It is believed that the attack by the immune system on the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin results in type 1 diabetes.
- It can be caused due to hereditary triggered by environmental factors.
- Type 2 diabetes is genetically linked very strongly. Those having a positive family history of diabetes are commonly known to develop type 2 diabetes.
- Obesity, high blood pressure, consumption of high-fat diet, over intake of alcohol, sedentary lifestyle, aging, and high blood triglyceride levels are some of the risk factors responsible for type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms
Type 1 Diabetes:
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually come very dramatically and suddenly.
- It is generally recognized in the early stage of life in association with an injury or illness like viral infection.
- Over stress can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis which causes vomiting and nausea followed by disturbances in potassium levels in blood and dehydration. If untreated, ketoacidosis can drag a victim to death or coma.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are often slight and can be ascribed to obesity or aging.
- For many years, a person may have type 2 diabetes but may not be even aware of.
- Those with type 2 diabetes may develop hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome. It is a condition in which the blood sugar level increases to a very high level. Thus, the body tries to remove the excess blood sugar level through urine and significantly increases the number of urination process further leading to dehydration.
- Stress and steroids can trigger development of type 2 diabetes rapidly
- If untreated, then type 2 diabetes can result in blindness, heart ailments, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Some of the symptoms which are common in both type 1 and 2 diabetes cases are loss of weight inexplicably, fatigue, polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyphagia (excessive eating), polyuria (excessive urination), delay in the healing of wounds, faint vision, infections, and disturbed mental status.
Diagnosis of diabetes
One can get to know whether he/she is a victim of diabetes by finding out if there is any excess amount of glucose in his body. This can be done by getting a sample of his/her urine tested in the laboratory followed by a blood test for confirming if the symptoms points out towards diabetes. Following are the ways through which you can determine if you are having prediabetes, diabetes or neither.
- The A1C test
Normal – less than 5.7%
Prediabetes – between 5.7% and 5.99 %
Diabetes – at least 6.5%
- The FPG (fasting plasma glucose) test
Normal – less than 100 mg/dl
Prediabetes – between 100mg/dl and 125.99 mg/dl
Diabetes – at least 126 mg/dl
If the patient has damaged fasting glucose, then the FPG reading would be abnormal.
- The OGTT (oral glucose tolerance test)
Normal – less than 140mg/dl
Prediabetes – between 140 mg/dl and 199.9 mg/dl
Diabetes – at least 200 mg/dl
If the patient has damaged glucose tolerance, then the OGIT reading would be abnormal.
Complications of Diabetes
In the end, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes lead to high blood sugar levels, a state called hyperglycemia. Later, hyperglycemia results in the damages of retina of the eye leading to blindness, the blood vessels of the nerves leading to foot wounds and ulcers. This further leads to amputation of foot and leg. It can damage the blood vessels of kidneys which results in kidney failure. It can also damage the nerves in the automatic nervous system that can result in paralysis of the stomach and failure to maintain heart rate and blood pressure. Diabetes also increases the formation of fatty plaques inside the arteries leading to blockage. Which as a result, causes heart attack, stroke, and reduces blood flow in the legs and arms. Other problems include infections, diabetic kitoacidosis and hypoglycemia. Sweating, dizziness, tremor of the hands, headache, and difficulty to concentrate are some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia.
Medical Treatment
The treatment of diabetes varies from person to person depending upon the type of diabetes, medical problems, age, and health at the time of diagnosis, and complications involved. Once diagnosed, the doctor will set goals for the patient regarding lifestyle changes, controlling blood sugar levels and treatment accordingly. The diabetes care team will educate the patient about his/her condition, the required treatment and other details which the patient has to aware of on daily basis like how to inject the insulin, it’s storage and etc. The diabetes care team which consists of specialists in the areas of neurology, diet, foot care and eye related diseases. This team will be monitoring the progress of the patient at regular intervals.
Prevention
Although type 2 diabetes can be prevented in some cases, prevention method for type 1 diabetes is yet to be discovered. However, here are few of the self-care tips which can be useful in keeping diabetes under control:
- Do not eat foods that are rich in fat. Control your weight to normal level by including high-fiber diets.
- Exercise regularly.
- Decrease the consumption of alcohol and put an end to smoking.
- Take all the medicines in time as directed by the doctor if you have high cholesterol or blood pressure.
- Check fasting glucose and two hours after ingesting certain amount of glucose depending upon the weight of the patient.
Those who are aware of being having diabetes should concentrate more towards preventing complications.
- This can be done by keeping a check on the blood sugar levels every day.
- Quitting smoking.
- Controlling weight.
- Reducing too much intake of salt and consuming sufficient amount of water.
- Increasing physical activity.
- Giving adequate care to the body and avoiding cuts and bruises.


 Cart : 0 items - $0.00
Cart : 0 items - $0.00