The noxious and lethal Ebola pandemic across the West African land is estimated to last for around twelve to eighteen moths which is a time span not previously anticipated for survival of the condition. It is also likely to infect thousands of more Ebola free individuals, before being subsided by any treatment if introduced.
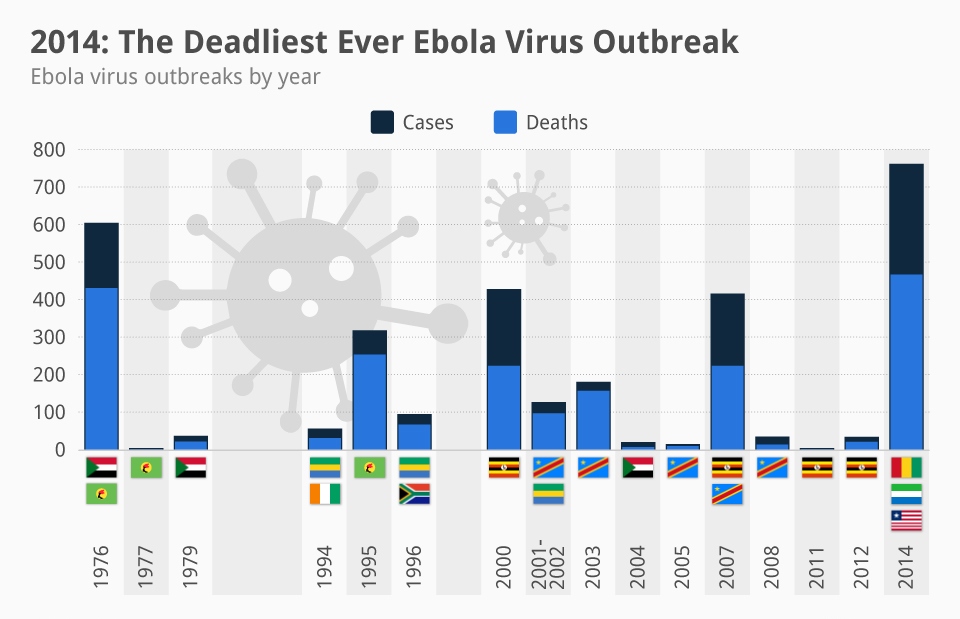 The number of Ebola positive cases recorded is said to be exceeding the WHO estimated rate of incidences and that too by far. WHO or World Health Organization predicted that the epidemic will come under control in nine months, and around 20,000 incidences in total will be recorded. However, the number is still increasing and there is no sign of relief.
The number of Ebola positive cases recorded is said to be exceeding the WHO estimated rate of incidences and that too by far. WHO or World Health Organization predicted that the epidemic will come under control in nine months, and around 20,000 incidences in total will be recorded. However, the number is still increasing and there is no sign of relief.
Introduction to Ebola:
Ebola is a rare disease which is said to have originated in Liberian region of Africa. The disease is resulted out of one of the viruses of Ebola (Tai Forest virus, Sudan Virus, Bundibugyo virus or Ebola Virus). The condition can spread from affected person to unaffected one through direct contact of broken skin or mucous membrane. The virus – which is potential to cause spread – is usually contained in affected individual’s urine, saliva, vomit, semen, feces or other body fluids. It may also spread due to direct contact to virus through contaminated objects such as needles or also through animals.
Individual affected with this condition may suffer from symptoms such as serve headache, pain in muscles, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in stomach, irrational bruising, unexplained bleeding, etc.
According to researchers from several universities around the world the current pace of affliction indicates that the virus can cause approx 20,000 victims in a month and not in total span of nine months as predicted by the WHO. Though there are consistent efforts by experts in covering all areas of pharmacology to deal with virus – such as medicine research and computer model generation, etc – no hope can be seen anywhere.
Though, previous epidemics were confined to only rural areas, the current pandemic – which is also considered as the largest outbreak ever – has affected people also in highly populated areas and some immiserate cities of the country like Monrovia. According to an expert involved in Computer Modeling of Ebola’s far-flung reach, there can be very little experts can do if the condition’s rate of incidence reaches around 100,000 or more.
The fact that rate of Ebola has begun to increase exponentially has worried the public health experts in Liberia. In recent statistics of the week, 400 new incidences of Ebola affliction were recorded, which is approx double the cases recorded in previous week. Another factor of worry is underreporting of the deaths caused due to Ebola, as out of 4366 recorded cases of Ebola only 2218 deaths were informed.
Despite of drastic efforts by the medical industry and feudal agencies, there are no signs of downturn of the outbreak. Experts working on computer modelling of the disease assert that the dreadful predictions are based on the current unmanageable and uncontrolled spread of Ebola. They also consoled that circumstances would improve if public health effort starts to improve. However, it was also said that the condition may aggravate or alleviate, but results of studies becomes uncertain as they dig deeper into the subject.
The spread of the disease is simple as it grows exponentially. However, according to a research professor from a university in Washington D.C, the WHO drafted estimates are conservative and latest predictions are more reasonable. It is said that the final recorded fatality rate may be much higher than any of the current estimates shared by agencies, unless an efficacious vaccine or treatment is made available.
Since, Ebola is spreading rapidly, some scientists are doubtful while others are determined and have an open mind; however, all are engaged in finding a cure for the fatal disease. Experts suggested following safety precautions as mentioned by the health organizations, with the fundamental precautionary measure being avoiding contact with body fluids of affected individual. This is because if the virus keeps spreading and covers a vast sector of the population, then it will mutate and become more contagious, making it difficult to bring down the morbidity rate.


 Cart : 0 items - $0.00
Cart : 0 items - $0.00