There are many organisms that cause infections and these infections take several routes to reach and infect the human beings both of which are explained in here.
An individual with an infection has another living thing inside hem/her which gets its nourishment via that individual; it colonizes that individual’s body and reproduces. An individual with this organism is known as the host; the germ / pathogen are called parasitic organism. It makes use of the host to feed and later on reproduce within host to a degree that the host’s health gets affected.
A living organism which colonizes and causes harm to its host’s health is generally known as a pathogen. Included in this category are:
- 1. Virus
- 2. Fungi
- 3. Bacteria
- 4. Prions
- 5. Viroids
All of us get infected at some point of time, but deal with them swiftly. Many people, however, are affected with chronic infections. Nearly all chronic infections come from viruses. Chronic microbe infections may affect sufferers with diabetes, in addition to individuals with weakened natural defenses.
Viral Infections
A person might get infected by a virus by:
- 1. Breathing in the virus
- 2. Getting bitten by contaminated bugs or parasites
- 3. By intimate contact
Some antiviral drugs might help; they either weaken the virus’ capability to reproduce, or raise the patient’s defense mechanisms.
Bacterial Infections
Bacteria can reside in almost any type of atmosphere, from really hot to cold, and even in radioactive waste. Numerous bacteria reside in the body, on our skin, throat, mouth, intestinal and urinary tracts – more often than not without leading to any injury to the host.
A comparatively small amount of bacteria bring about ailments in humans. Probably the most deadly disorders and harmful epidemics in history happen to be brought on by bacteria, including:
- 1. Cholera
- 2. Dysentery
- 3. Plague
- 4. Pneumonia
- 5. Tuberculosis
- 6. Typhoid
Fungal Infection
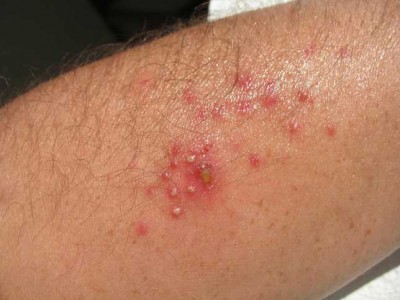
Mycosis is really an infection in or on the area of the body, or perhaps a disease, the result of a fungus. A few fungi replicate through really small airborne spores which individuals either inhale or detect their skin – i.e. most fungal infections begin in the lungs or even the skin.
You will find 3 kinds of fungal infections of your skin:
- 1. Superficial mycoses – restricted to the top of hair and skin.
- 2. Cutaneous mycoses – takes place deeper within the skin, within the epidermis
- 3. Subcutaneous mycoses – these kinds of infections go deeper in to the skin, such as the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, in addition to muscle as well as fascia.
Prion Disease
A prion is a contagious agent composed primarily of protein (neither bacterial nor fungal) – it has no genetic content. It happens typically as a benign form, however when it retracts into an unnatural shape it becomes a rogue agent and affects the brain’s structure or any other areas of the central nervous system. All types of prion infections are presently untreatable and also fatal.
Routes Of Infections
Given below is the list of ways infection spreads:
Airborne: A few infections are propagated when the infected individual sneezes or coughs tiny air-borne droplets. These droplets in mid-air might be breathed in directly by someone or else indirectly via touching objects with the tiny droplets in it.
Food / Waterborne: These illnesses are triggered from intake of water or foods contaminated with certain disease-causing micro-organisms or their toxins. Frequently these bacterial infections will also be distributes through the fecal-oral path.
Fecal-Oral: Some bacterial infections are dispersed whenever microscopic amounts of feces from the infected individual somehow enter another person’s body through the mouth. The feces may be passed through soiled fingers to the mouth area or by means of surfaces, meals or drinking water soiled with feces.
Urine: Some bacterial infections are dispersed whenever urine is actually transferred through soiled fingers or items towards the mouth area.
Body Fluids Or Blood: A few infections are distributed when bloodstream or any other body fluids like phlegm from an infected individual contact the blood or body fluids of the uninfected person via needles or blades.
Contact With Skin / Mucous Membrane: A few infections are distributed directly whenever skin / mucous membrane touches other skin / mucous membrane. These infections are also dispersed when and skin / mucous membrane comes in contact with contaminated areas.
Sexually Transmitted Infections: These types of infections are commonly transmitted through sexual intimacy.
Saliva: A few infections are distributed by immediate connection with spit for example when kissing.


 Cart : 0 items - $0.00
Cart : 0 items - $0.00