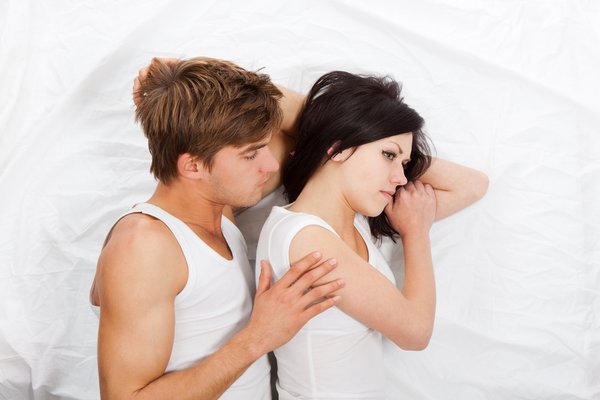
The medical word for painful intercourse is dyspareunia which is generally defined as relentless genital pain that an individual feels just before, maybe during or after intercourse with his or her partner. It is essential to talk to the doctor if you are experiencing dysaprenuia or painful intercourse tremendously. There are treatments which focus on this underlying cause, and can help you eliminate or probably reduce this problem of painful intercourse.
Types
- Different types of pain a woman can undergo:
- A kind of Pain can probably occur when a woman feels pain at the vulva, probably at the opening of the vagina or may be deep inside is known as Vulvar pain.
- The pain felt when at times the vagina is dry and it lacks moisture and that could be one of the reasons for pain is known as vaginal pain.
- Pain caused due to some serious internal injury caused is known as deep pain. Women might feel the pain when a man’s penis touches her cervix.
Symptoms
Symptoms of painful intercourse are:
- When you experience pain only during sexual penetration (entry)
- Experiencing pain with every penetration you undergo with your partner, even while putting in a tampon
- Pain only with certain partners or probably just under certain circumstances
- When you experience a new kind of pain after previously pain-free intercourse
- Deep pain during thrusting, which is frequently described as “something being bumped”
- You might even feel burning sensation, pain or aching pain.
Causes
There are many causes of painful intercourse. There may be emotional factors which are associated with numerous types of painful intercourse.
You might feel the pain during penetration which may be associated with a range of factors:
Insufficient lubrication:
It is generally the result of not enough foreplay. Insufficient lubrication is commonly caused by a drop in estrogen levels after childbirth or may happen during breast-feeding.
Injury, trauma or irritation:
Trauma or an injury includes irritation caused from an accident or may be pelvic surgery. It can also be caused due to female circumcision or a congenital abnormality.
Inflammation, infection or skin disorder:
Any infection in your genital area or inflammation caused in the urinary tract can cause painful intercourse. Eczema or any other skin problems in your genital area can also be reason for your problem.
Certain illnesses and conditions:
There is a list of certain illnesses which includes endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease. An Illness under this also includes uterine prolapse, cystitis, hemorrhoids and ovarian cysts.
Emotional factors:
At times a person must be undergoing some kind of stress or emotional instability due to which an intercourse must be painful. Emotions or emotionally disturbed mind or excessive stress are one of the reasons where the individual becomes extremely entangled with sexual activity. Some of the emotional factors are:
- Psychological Problems. Anxiety, attacks of depression, any major concerns about your physical form, any fear of intimacy that an individual possesses or relationship problems one goes through. All these aspects lower down the arousal level and can lead to tremendous pain during intercourse.
- Stress. Your pelvic floor muscles at times tighten in response to the stress you may be going through in your life. This can contribute to pain during intercourse.
- History Of Sexual Abuse. Many women with dyspareunia generally don’t have a history of sexual exploitation. If any person is sexually abused, it also may play a role in painful intercourse.
Diagnosis / Tests
Medical history: a doctor can check the medical history of the patient in order to know if he or she has gone through any sexual abuse or what problems a couple has faced during their sexual life.
A pelvic examination: In a pelvic examination, the doctor can probably check for the signs of skin irritation, or any kind of infection caused due to some reason or anatomical problems. The doctor can also try to identify the exact location of your pain by applying moderate pressure to the genital area and your pelvic muscles.
Other tests: any other tests can also be carried out by your doctor as he or she may feel right.
Treatments
Your doctor may give you a proper medication so that your painful intercourse problem can be cured. Medications may also cause lubrication problems as studied by researchers. At times, it can also be cured by a tablet, some kind of cream or probably a flexible ring that releases small amounts of estrogen directly to your vagina.
There are different types of therapy also which oe can undergo:
1. Sex therapy
2. Desensitization therapy
Prevention
You can prevent painful intercourse by communicating with your partner as to the problem you are facing while sex. You can also do more of foreplay as it would naturally help her to be more lubricated. Women need a lot more foreplay than men before sex so it is better to take it slower. This is one of the natural reasons how pain during sex can be avoided.
Home Remedies
While you and your partner feel pain during intercourse you can make a few changes in your sex routine like:
- Switch Positions: you can try changing positions as that may help in reducing the pain. You can also try being on top of your spouse during intercourse. Women generally have more control in this kind of position.
- Communicate: tell your partner to go slow if you are experiencing pain and discomfort. Don’t hesitate.
- Do Not Rush: do not rush to d sex. Foreplay can help you with natural lubrication then probably you might not feel the pain during sex. Take it slow.
Warnings / Precautions
Certain kinds of precautions are to be undertaken while you and your spouse have sex like do not force yourself into sex. Make sure your partner and your partner are comfortable and it doesn’t pain so have enough foreplay before moving into sex.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Consulting your doctor is very important in order to know what is the cause and reason for such painful intercourse.
- One can ask his doctor what are the reasons for this illness?
- How can such reasons be avoided as it can cause problems in one’s sexual life?
- What are the precautions to be taken?
- Can this illness be recovered from or cured permanently?


 Cart : 0 items - $0.00
Cart : 0 items - $0.00